As pirates, we all love plundering, we all love raiding, but mostly, we all love bounties, especially Bug Bounties. Let’s talk about it.

Bug Bounties are reward-based programs that helps companies, websites, organizations and software developers to strengthen their protection layers and it has become a big part of the cyber management and information security strategy in organizations in recent years.
Find the Bug – Get the Bounty
Yes, like the name suggests, as an incentive, people will be rewarded for finding any software-related bugs, which acts as an enhancement to their motivation, yes just picture a perfect world where you get paid for hacking…
The idea of the bug bounty was first proposed in 1983 by the company Hunter & Ready which announced that it would give a Volkswagen beetle to anyone who found a bug in its real-time operating system – VRTX. It’s also worth mentioning that the bugs being found are not only security-related bugs, it ranges from visual bugs to UX based issues, you get paid for everything (if they offered to pay for it of course).
The two main goals of Bug Bounty are :
- To motivate security researchers to investigate the websites and services of the companies, to report the bugs before they are published to the public, thus preventing the use and abuse of the breach that was found.
- To make it so that even Black Hat Hackers who find a certain breach, will not spread it to the general public, but will report it to the company, due to the fact that they are expected to receive a compensation / award for doing so.
However, these programs are also controversial. Some argue that they give hackers some sort of “Seal of approval” to hack into systems. Therefore, most of these programs are defined using precise and strict procedures and protocolos. Apple, for example, started its bug bounty in a limited format for dozens of researchers only and only later opened the program to the general public.
What do I need to know in order to be able to participate in such programs?
Firstly, a good “Bounty Hunter” must think like an attacker. Since what he actually does is attack and find a certain security loophole. He needs to have an in-depth understanding of cyber security in general, ability to identify and monitor events, he should be capable of initiating cyber attacks, understanding defense mechanisms, familiarity with information systems as well as knowing to use certain applications, and, It’s also important to be proficient in different languages such as JAVA, JavaScript (especially for Web-based), Python and even languages responsible only for editing such as HTML.
Popular Bug bounty programs and stories
In 2013, Google announced that it would expand its Bug Bounty program, which until then, the bug bounties dealt with bugs and “security holes” in the company’s prominent services only. Starting in 2013, the program would be expanded, so that it would also include a selection of Google applications whose impact and their importance is low compared to the Chrome Operating System. In 2019, Google expanded the program even further and offered incentives even for those who find bugs and security holes in most of the applications that can be downloaded in the Google Play store. The payment offered by Google to finders of loopholes ranges from 500 to 50,000 dollars depending on the severity of the bug.
Microsoft also has its own bug bounty program, in which the amount of prizes ranges from 15,000 to 300,000 dollars. Between July 1, 2018 and January 1, 2019, Microsoft paid royalties to security researchers, totaling in 4.4 million dollars!
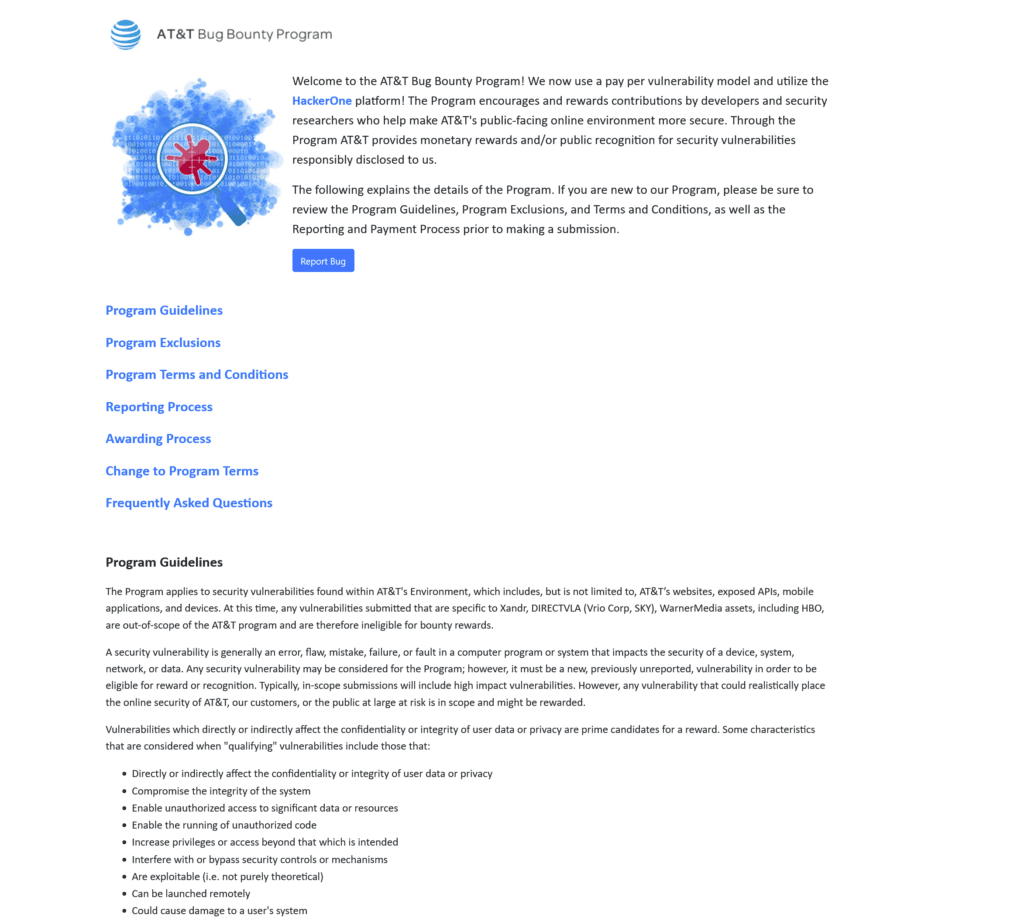
For full program description go here
Jani, a 10-year-old Finnish boy, won a pampering gift from Facebook at the beginning of May, 2016: $10,000. According to the tech sites that reported the reward, Jani received the money in exchange for finding a security breach in the Facebook-owned Instagram app. The vulnerability he found in the software allowed him to delete messages from other users on the network. After proving to Facebook the feasibility of exploiting this weakness in a dedicated account, he received the reward.
Here’s a list of public Bug Bounty programs for, you know, just in case.
Stay safe, choose Cytrix.